Heel pain is most often caused by plantar fasciitis, a condition that is sometimes also called heel spur syndrome when a spur is present. Heel pain may also be due to other causes, such as a stress fracture, tendonitis, arthritis, nerve irritation, or, rarely, a cyst.
Because there are several potential causes, it is important to have heel pain properly diagnosed. A foot and ankle surgeon is able to distinguish between all the possibilities and determine the underlying source of your heel pain.
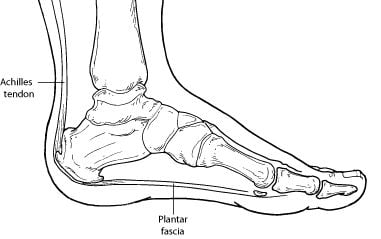 What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the band of tissue (the plantar fascia) that extends from the heel to the toes. In this condition, the fascia first becomes irritated and then inflamed, resulting in heel pain.
Causes
The most common cause of plantar fasciitis relates to faulty structure of the foot. For example, people who have problems with their arches, either overly flat feet or high-arched feet, are more prone to developing plantar fasciitis.
Wearing non-supportive footwear on hard, flat surfaces puts abnormal strain on the plantar fascia and can also lead to plantar fasciitis. This is particularly evident when one’s job requires long hours on the feet. Obesity may also contribute to plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are:
- Pain on the bottom of the heel
- Pain that is usually worse upon arising
- Pain that increases over a period of months
People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they’ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
To arrive at a diagnosis, the foot and ankle surgeon will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the surgeon rules out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis.
In addition, diagnostic imaging studies such as x-rays or other imaging modalities may be used to distinguish the different types of heel pain. Sometimes heel spurs are found in patients with plantar fasciitis, but these are rarely a source of pain. When they are present, the condition may be diagnosed as plantar fasciitis/heel spur syndrome.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Treatment of plantar fasciitis begins with first-line strategies, which you can begin at home:
- Stretching exercises. Exercises that stretch out the calf muscles help ease pain and assist with recovery.
- Avoid going barefoot. When you walk without shoes, you put undue strain and stress on your plantar fascia.
- Ice. Putting an ice pack on your heel for 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce inflammation. Place a thin towel between the ice and your heel; do not apply ice directly to the skin.
- Limit activities. Cut down on extended physical activities to give your heel a rest.
- Shoe modifications. Wearing supportive shoes that have good arch support and a slightly raised heel reduces stress on the plantar fascia.
- Medications. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
If you still have pain after several weeks, see your foot and ankle surgeon, who may add one or more of these treatment approaches:
- Padding and strapping. Placing pads in the shoe softens the impact of walking. Strapping helps support the foot and reduce strain on the fascia.
- Orthotic devices. Custom orthotic devices that fit into your shoe help correct the underlying structural abnormalities causing the plantar fasciitis.
- Injection therapy. In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used to help reduce the inflammation and relieve pain.
- Removable walking cast. A removable walking cast may be used to keep your foot immobile for a few weeks to allow it to rest and heal.
- Night splint. Wearing a night splint allows you to maintain an extended stretch of the plantar fascia while sleeping. This may help reduce the morning pain experienced by some patients.
- Physical therapy. Exercises and other physical therapy measures may be used to help provide relief.
When Is Surgery Needed?
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you.
Long-term Care
No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
-
Ulcers/Wounds
Ulcers, which are open sores in the skin, occur when the outer layers of the skin are injured and the deeper tissues become exposed. They can be caused by excess pressure due to ill-fitting shoes, long periods in bed, or after an injury that breaks the skin. Ulcers are commonly seen in patients who have
Read more -
Varicose Veins
Category: Bone/Joint/Tendon
Varicose veins are usually due to improperly functioning valves within the veins. The veins typically appear prominent or look "raised." The condition can cause swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet. The skin may become discolored due to leakage of blood into the surrounding tissues, and ulcers may
Read more -
Volleyball Injuries to the Foot and Ankle
Category: Fitness and Your Feet
The repetitive jumping and side to side movements required in volleyball increase the risk of injuries to the foot and ankle. Volleyball players should be aware of the following: Inversion ankle sprains are a common injury in this sport. Ankle sprains should be evaluated by a foot and ankle surgeon
Read more -
Warts
Category: Nails and Skin
What is a Plantar Wart? A wart is a small growth on the skin that develops when the skin is infected by a virus. Warts can develop anywhere on the foot, but typically they appear on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. Plantar warts most commonly occur in children, adolescents, and the elderly. There
Read more -
Weak Ankles
Category: Bone/Joint/Tendon, Ankle
Weak ankles may be a result of previous ankle injuries, but in some cases they are a congenital (at birth) condition. The ankles are sore, and “give way” easily while standing, walking, or doing other activities. When an ankle is injured, it may take a few weeks to many months to fully heal. Often,
Read more -
Webbed Toes
Category: Bone/Joint/Tendon
Webbed toes (also known as syndactyly) is a rare condition seen in approximately one in 2,000 births. Those with this condition have two or more toes that are partially or fully joined by a flexible skin bridge. Syndactyly most commonly affects the second and third toes, but it can occur between
Read more -
White Toenails
Category: Nails and Skin
Webbed toes (also known as syndactyly) is a rare condition seen in approximately one in 2,000 births. Those with this condition have two or more toes that are partially or fully joined by a flexible skin bridge. Syndactyly most commonly affects the second and third toes, but it can occur between
Read more -
Wounds-Puncture
Category: Nails and Skin
What Is a Puncture Wound? Puncture wounds are not the same as cuts. A puncture wound has a small entry hole caused by a pointed object, such as a nail that you’ve stepped on. In contrast, a cut is an open wound that produces a long tear in the skin. Puncture wounds require different treatment
Read more -
Wounds/Uclers
Category: Nails and Skin
Ulcers, which are open sores in the skin, occur when the outer layers of the skin are injured and the deeper tissues become exposed. They can be caused by excess pressure due to ill-fitting shoes, long periods in bed, or after an injury that breaks the skin. Ulcers are commonly seen in patients who have
Read more -
Yellow Toenails
Category: Nails and Skin
The most common cause of yellow discoloration in the toenails is a fungal infection. The fungus often develops underneath the nail, resulting in it becoming thick, raised, and yellow in color. Other potential causes for yellow discoloration of the nail include diabetes mellitus and lymphedema (chronic
Read more
